This post may contain affiliate links. For more info, please read our full disclosure here
Ketones and ketosis are words you will constantly have to deal with on the ketogenic diet. Understanding them, knowing what they are and how they work is essential to succeed on keto.
They are essential parts of the ketogenic diet, getting them right will make things easier.
Ketones and ketosis
Ketosis
The ketogenic diet is a low carb, moderate protein and high fat way of eating. On the ketogenic diet, you are to reduce your carb intake to the extent where your body turns to its next readily available fuel source, which is fats.
The human body has the ability to run on 2 main sources of energy
- Glucose(gotten from carbohydrates)
- Ketones(gotten from fats and fatty acids)
When you follow a standard high carb diet, your body converts the carbs into glucose to use for energy.
When you follow a high fat diet like the ketogenic diet, your carb intake is reduced to a point where your body turns to fats being its alternative energy source.
Being in ketosis has a lot of health benefits. To achieve ketosis on the ketogenic diet, you need to follow the keto macronutrient ratios.
The macronutrient ratios for the ketogenic diet is about 70% fats, 20 – 25% protein and 5 – 10% carbohydrates.
Your body has the ability not only to function well but to even function better following these ratios.
Ketones
Ketones are the fuel source for people in ketosis. They are produced from the breakdown of fats and fatty acids. There are 3 ketones mainly produced in ketosis.
- Acetoacetate
- Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB)
- Acetone
Acetoacetate is manly used by the cell and over time gets converted to a more efficient form, BHB the more fat adapted you become. Acetone is mainly excreted from the body through your urine and your breath.
Ketones have been proven to be a highly efficient fuel source, even more efficient than glucose. However, this doesn’t mean that there is no use for glucose.
Certain cells of the body still require glucose and even a tiny portion of the fats you consume is converted into glucose.
Ideally, following the macronutrient ratios for the ketogenic diet gives your body all it needs to be at its peak. Even better than it would be on a high carb diet
What your ketone levels say
Your ketone levels indicate whether you are in ketosis or not and how well your body is burning fat for energy. Also, achieving and maintaining ketosis are important hallmarks of the ketogenic diet.
Certain things affect your ketone levels like
- Exercise
- Glucose production
- Hormonal changes
This doesn’t mean you should obsess over your ketone levels. But knowing your ketone levels can help you make diet and lifestyle changes to help you get into optimal ketosis and fully enjoy the benefits of the ketogenic diet.
Eating the right amount of macronutrients for your body will keep you in ketosis and keep you fat adapted.
Measuring ketosis

As stated earlier, knowing your ketone levels will help you determine if you are in ketosis or not and help you make the necessary steps to get your body in place. There are 3 main ways you can use to measure ketosis.
- Urine testing
- Breath testing
- Blood testing
Urine testing
You can test your ketosis levels through your urine. This is because unused acetoacetate is removed from the body through the urine.
Urine strips are used for testing urine ketone levels and can help determine if you are in ketosis. However, it is not too accurate as your body releases less acetone when you become more fat-adapted. So its important to take note of that.
Breath testing
Another way to measure ketosis is by breath testing. As stated earlier, acetone is removed from the body through your breath and urine.
When measuring ketosis through breath testing, a breath ketone meter is used. It measures the amount of acetone in your breath which indicates your level of ketosis.
Breath testing seems pretty accurate, at least more than urine testing, although not as accurate as blood testing. But still keep in mind that the readings may become slightly lower once you’re fully fat adapted.
Blood testing
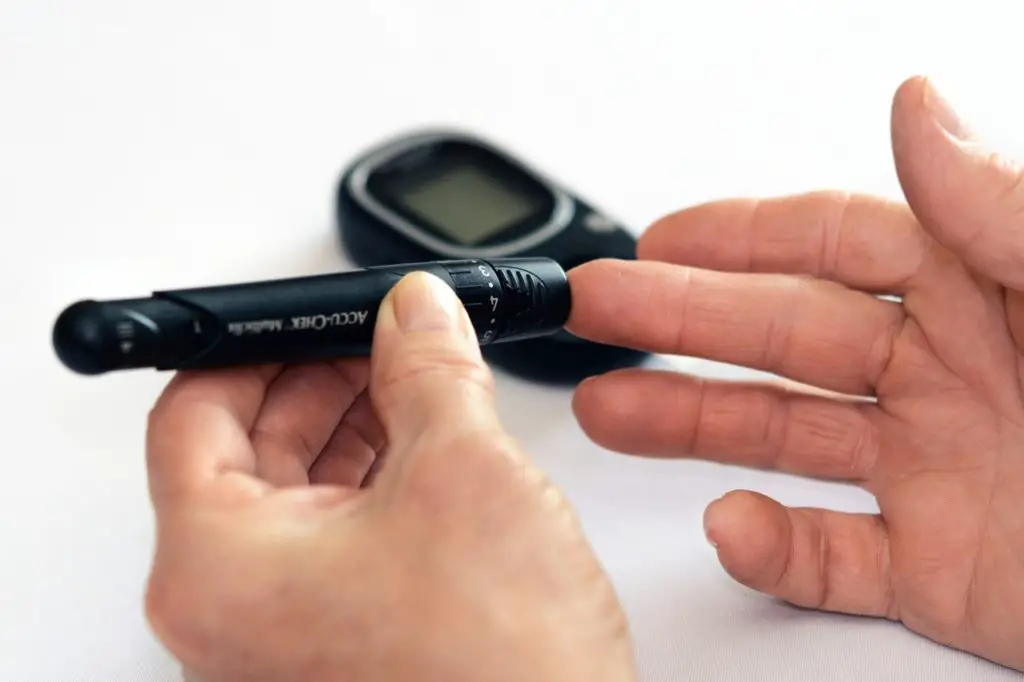
Blood testing is the most accurate way to measure ketosis. Unlike the other 2 methods, it measures the amount of ketones directly in the bloodstream.
To measure ketosis through blood testing, a blood meter is used. To measure ketosis using a blood meter, you slightly prick your finger and draw blood for the reading.
When using a blood ketosis meter, the reading determines your level of ketosis
- 0.5 – 1.5mmol/L or 50 – 150mg/dL indicates the beginning on nutritional ketosis
- 1.5 – 3.0 indicates optimal ketosis. You should aim for this range
- 3.0 – 10.0 indicates starvation ketosis. You should avoid this
- 10.0 and above indicates ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis

Ketoacidosis happens when there is an excessive amount of ketones accumulating in the blood and is a very dangerous condition. However, as similar as it may sound with ketosis, ketosis and ketoacidosis are different.
On the ketogenic diet, your liver won’t produce way more ketones than the body needs. Ketoacidosis occurs in type 1 and some type 2 diabetic patients due to poor blood sugar levels.
In simple terms, being on the ketogenic diet will not cause ketoacidosis
For more information on ketoacidosis and how different it is from ketosis, click here
Takeaway
Ketones and ketosis are important aspects of the ketogenic diet. Understanding them and how they work will help you take the right steps and make the right changes that will ensure success on keto.
Following your macronutrient needs, you can achieve and maintain ketosis and knowing your ketone levels will help you take important steps towards achieving your goals on the ketogenic diet. Cheers.
